 | |
| reproducibility |
It is the degree of
closeness with which a given value may be repeatedly measured. It may be
specified interms of units for a given period of time. The perfect
reproducibility indicates no drift in the instrument.
The
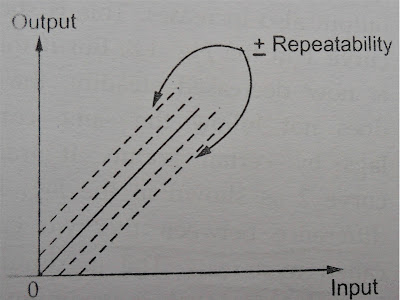
repeatability is defined as variation of scale reading and in random in nature.
Both reproducibility and the repeatability are measure of the closeness with
which a given input may be measured again and again. The fig shows the input
and output relationship with positive and negative repeatability.
Stability
The ability of an instrument
to retain its performance throughout its specified operating life and storage
life is defined as its stability.
Tolerance:
The maximum allowable error
in the measurement is specified interms of some value which is called
tolerance. This is closely related to accuracy.
The
tolerance indicates the maximum allowable deviation of a manufactured component
from a specified value.
Rang
of span
The minimum and maximum value
of a quantity for which an instrument is designed to measure is called its
range or span. Sometimes the accuracy is specified interms of range or span of
an instrument.
Bias
The constant error which
exists over the full range of measurement of an instrument is called bias. Such
a bias can be completely eliminated by calibration. The zero error is an
example of bias which can be moved by
calibration
.
Hysteresis
If
the input to the instrument is increased from a negative value, the output also
increases. But the curve is now decreased steadily. The output does not follow
the same curve but lags by certain value. It traces the curve 2. The difference
between the two curves is called hysteresis. The maximum input Hysteresis and
maximum output Hysteresis are shown. These are generally expressed as the
percentage of the full scale reading.
 |
| Instrument with hysteresis |
Dead
space
In some instruments, it is
possible that till input increases beyond certain value, the output does not
change. So for certain range of input values there is no change in output. This
range of input is called dead space. There is possibility that instrument
without hysteresis may show the dead space in their output characteristics.
Backlash in gears is a good example which causes the dead space.
Span
drift or sensitivity drift


0 comments:
Comment Here...